在RedMonk发布的2015年1月编程语言排行榜中,Swift采纳率排名迅速飙升,从刚刚面世时的68位跃至22位,Objective-C仍然稳居TOP10,而JavaScript则凭借着其在iOS平台上原生体验优势成为了年度最火热的编程语言。
而早在2013年苹果发布的OS X Mavericks和iOS 7两大系统中便均已加入了JavaScriptCore框架,能够让开发者轻松、快捷、安全地使用JavaScript语言编写应用。不论叫好叫骂,JavaScript霸主地位已成事实。开发者们趋之若鹜,JS工具资源层出不穷,用于OSX和iOS系统等高速虚拟机也蓬勃发展起来。
JSContext/JSValue
JSContext即JavaScript代码的运行环境。一个Context就是一个JavaScript代码执行的环境,也叫作用域。当在浏览器中运行JavaScript代码时,JSContext就相当于一个窗口,能轻松执行创建变量、运算乃至定义函数等的JavaScript代码:
//Objective-C
JSContext *context = [[JSContext alloc] init];
[context evaluateScript:@"var num = 5 + 5"];
[context evaluateScript:@"var names = ['Grace', 'Ada', 'Margaret']"];
[context evaluateScript:@"var triple = function(value) { return value * 3 }"];
JSValue *tripleNum = [context evaluateScript:@"triple(num)"];
//Swift
let context = JSContext()
context.evaluateScript("var num = 5 + 5")
context.evaluateScript("var names = ['Grace', 'Ada', 'Margaret']")
context.evaluateScript("var triple = function(value) { return value * 3 }")
let tripleNum: JSValue = context.evaluateScript("triple(num)")
像JavaScript这类动态语言需要一个动态类型(Dynamic Type), 所以正如代码最后一行所示,JSContext里不同的值均封装在JSValue对象中,包括字符串、数值、数组、函数等,甚至还有Error以及null和undefined。
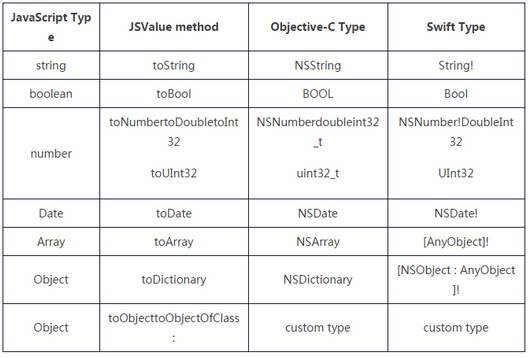
JSValue包含了一系列用于获取Underlying Value的方法,如下表所示:
想要检索上述示例中的tripleNum值,只需使用相应的方法即可:
//Objective-C
NSLog(@"Tripled: %d", [tripleNum toInt32]);
// Tripled: 30
//Swift
println("Tripled: \(tripleNum.toInt32())")
// Tripled: 30
下标值(Subscripting Values)
通过在JSContext和JSValue实例中使用下标符号可以轻松获取上下文环境中已存在的值。其中,JSContext放入对象和数组的只能是字符串下标,而JSValue则可以是字符串或整数下标。
//Objective-C
JSValue *names = context[@"names"];
JSValue *initialName = names[0];
NSLog(@"The first name: %@", [initialName toString]);
// The first name: Grace
//Swift
let names = context.objectForKeyedSubscript("names")
let initialName = names.objectAtIndexedSubscript(0)
println("The first name: \(initialName.toString())")
// The first name: Grace
而Swift语言毕竟才诞生不久,所以并不能像Objective-C那样自如地运用下标符号,目前,Swift的方法仅能实现objectAtKeyedSubscript()和objectAtIndexedSubscript()等下标。
函数调用(Calling Functions)
我们可以将Foundation类作为参数,从Objective-C/Swift代码上直接调用封装在JSValue的JavaScript函数。这里,JavaScriptCore再次发挥了衔接作用。
//Objective-C
JSValue *tripleFunction = context[@"triple"];
JSValue *result = [tripleFunction callWithArguments:@[@5] ];
NSLog(@"Five tripled: %d", [result toInt32]);
//Swift
let tripleFunction = context.objectForKeyedSubscript("triple")
let result = tripleFunction.callWithArguments([5])
println("Five tripled: \(result.toInt32())")
异常处理(Exception Handling)
JSContext还有一个独门绝技,就是通过设定上下文环境中exceptionHandler的属性,可以检查和记录语法、类型以及出现的运行时错误。exceptionHandler是一个回调处理程序,主要接收JSContext的reference,进行异常情况处理。
//Objective-C
context.exceptionHandler = ^(JSContext *context, JSValue *exception) {
NSLog(@"JS Error: %@", exception);
};
[context evaluateScript:@"function multiply(value1, value2) { return value1 * value2 "];
// JS Error: SyntaxError: Unexpected end of script
//Swift
context.exceptionHandler = { context, exception in
println("JS Error: \(exception)")
}
context.evaluateScript("function multiply(value1, value2) { return value1 * value2 ")
// JS Error: SyntaxError: Unexpected end of script
JavaScript函数调用
了解了从JavaScript环境中获取不同值以及调用函数的方法,那么反过来,如何在JavaScript环境中获取Objective-C或者Swift定义的自定义对象和方法呢?要从JSContext中获取本地客户端代码,主要有两种途径,分别为Blocks和JSExport协议。
Blocks (块)
在JSContext中,如果Objective-C代码块赋值为一个标识符,JavaScriptCore就会自动将其封装在JavaScript函数中,因而在JavaScript上使用Foundation和Cocoa类就更方便些——这再次验证了JavaScriptCore强大的衔接作用。现在CFStringTransform也能在JavaScript上使用了,如下所示:
//Objective-C
context[@"simplifyString"] = ^(NSString *input) {
NSMutableString *mutableString = [input mutableCopy];
CFStringTransform((__bridge CFMutableStringRef)mutableString, NULL, kCFStringTransformToLatin, NO);
CFStringTransform((__bridge CFMutableStringRef)mutableString, NULL, kCFStringTransformStripCombiningMarks, NO);
return mutableString;
};
NSLog(@"%@", [context evaluateScript:@"simplifyString('?????!')"]);
//Swift
let simplifyString: @objc_block String -> String = { input in
var mutableString = NSMutableString(string: input) as CFMutableStringRef
CFStringTransform(mutableString, nil, kCFStringTransformToLatin, Boolean(0))
CFStringTransform(mutableString, nil, kCFStringTransformStripCombiningMarks, Boolean(0))
return mutableString
}
context.setObject(unsafeBitCast(simplifyString, AnyObject.self), forKeyedSubscript: "simplifyString")
println(context.evaluateScript("simplifyString('?????!')"))
// annyeonghasaeyo!
需要注意的是,Swift的speedbump只适用于Objective-C block,对Swift闭包无用。要在一个JSContext里使用闭包,有两个步骤:一是用@objc_block来声明,二是将Swift的knuckle-whitening unsafeBitCast()函数转换为 AnyObject。
内存管理(Memory Management)
代码块可以捕获变量引用,而JSContext所有变量的强引用都保留在JSContext中,所以要注意避免循环强引用问题。另外,也不要在代码块中捕获JSContext或任何JSValues,建议使用[JSContext currentContext]来获取当前的Context对象,根据具体需求将值当做参数传入block中。
JSExport协议
借助JSExport协议也可以在JavaScript上使用自定义对象。在JSExport协议中声明的实例方法、类方法,不论属性,都能自动与JavaScrip交互。文章稍后将介绍具体的实践过程。
JavaScriptCore实践
我们可以通过一些例子更好地了解上述技巧的使用方法。先定义一个遵循JSExport子协议PersonJSExport的Person model,再用JavaScript在JSON中创建和填入实例。有整个JVM,还要NSJSONSerialization干什么?
PersonJSExports和Person
Person类执行的PersonJSExports协议具体规定了可用的JavaScript属性。,在创建时,类方法必不可少,因为JavaScriptCore并不适用于初始化转换,我们不能像对待原生的JavaScript类型那样使用var person = new Person()。
//Objective-C
// in Person.h -----------------
@class Person;
@protocol PersonJSExports @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *lastName;
@property NSInteger ageToday;
- (NSString *)getFullName;
// create and return a new Person instance with `firstName` and `lastName`
+ (instancetype)createWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName lastName:(NSString *)lastName;
@end
@interface Person : NSObject @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *lastName;
@property NSInteger ageToday;
@end
// in Person.m -----------------
@implementation Person
- (NSString *)getFullName {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", self.firstName, self.lastName];
}
+ (instancetype) createWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName lastName:(NSString *)lastName {
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
person.firstName = firstName;
person.lastName = lastName;
return person;
}
@end
//Swift
// Custom protocol must be declared with `@objc`
@objc protocol PersonJSExports : JSExport {
var firstName: String { get set }
var lastName: String { get set }
var birthYear: NSNumber? { get set }
func getFullName() -> String
/// create and return a new Person instance with `firstName` and `lastName`
class func createWithFirstName(firstName: String, lastName: String) -> Person
}
// Custom class must inherit from `NSObject`
@objc class Person : NSObject, PersonJSExports {
// properties must be declared as `dynamic`
dynamic var firstName: String
dynamic var lastName: String
dynamic var birthYear: NSNumber?
init(firstName: String, lastName: String) {
self.firstName = firstName
self.lastName = lastName
}
class func createWithFirstName(firstName: String, lastName: String) -> Person {
return Person(firstName: firstName, lastName: lastName)
}
func getFullName() -> String {
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
}
配置JSContext
创建Person类之后,需要先将其导出到JavaScript环境中去,同时还需导入Mustache JS库,以便对Person对象应用模板。
//Objective-C
// export Person class
context[@"Person"] = [Person class];
// load Mustache.js
NSString *mustacheJSString = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:... encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
[context evaluateScript:mustacheJSString];
//Swift
// export Person class
context.setObject(Person.self, forKeyedSubscript: "Person")
// load Mustache.js
if let mustacheJSString = String(contentsOfFile:..., encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding, error:nil) {
context.evaluateScript(mustacheJSString)
}
JavaScript数据&处理
以下简单列出一个JSON范例,以及用JSON来创建新Person实例。
注意:JavaScriptCore实现了Objective-C/Swift的方法名和JavaScript代码交互。因为JavaScript没有命名好的参数,任何额外的参数名称都采取驼峰命名法(Camel-Case),并附加到函数名称上。在此示例中,Objective-C的方法createWithFirstName:lastName:在JavaScript中则变成了createWithFirstNameLastName()。
//JSON
[
{ "first": "Grace", "last": "Hopper", "year": 1906 },
{ "first": "Ada", "last": "Lovelace", "year": 1815 },
{ "first": "Margaret", "last": "Hamilton", "year": 1936 }
]
//JavaScript
var loadPeopleFromJSON = function(jsonString) {
var data = JSON.parse(jsonString);
var people = [];
for (i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
var person = Person.createWithFirstNameLastName(data[i].first, data[i].last);
person.birthYear = data[i].year;
people.push(person);
}
return people;
}
动手一试
现在你只需加载JSON数据,并在JSContext中调用,将其解析到Person对象数组中,再用Mustache模板渲染即可:
//Objective-C
// get JSON string
NSString *peopleJSON = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:... encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
// get load function
JSValue *load = context[@"loadPeopleFromJSON"];
// call with JSON and convert to an NSArray
JSValue *loadResult = [load callWithArguments:@[peopleJSON]];
NSArray *people = [loadResult toArray];
// get rendering function and create template
JSValue *mustacheRender = context[@"Mustache"][@"render"];
NSString *template = @"{{getFullName}}, born {{birthYear}}";
// loop through people and render Person object as string
for (Person *person in people) {
NSLog(@"%@", [mustacheRender callWithArguments:@[template, person]]);
}
// Output:
// Grace Hopper, born 1906
// Ada Lovelace, born 1815
// Margaret Hamilton, born 1936
//Swift
// get JSON string
if let peopleJSON = NSString(contentsOfFile:..., encoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding, error: nil) {
// get load function
let load = context.objectForKeyedSubscript("loadPeopleFromJSON")
// call with JSON and convert to an array of `Person`
if let people = load.callWithArguments([peopleJSON]).toArray() as? [Person] {
// get rendering function and create template
let mustacheRender = context.objectForKeyedSubscript("Mustache").objectForKeyedSubscript("render")
let template = "{{getFullName}}, born {{birthYear}}"
// loop through people and render Person object as string
for person in people {
println(mustacheRender.callWithArguments([template, person]))
}
}
}
// Output:
// Grace Hopper, born 1906
// Ada Lovelace, born 1815
// Margaret Hamilton, born 1936